Acoustic Wave Therapy (AWT) and Shockwave Therapy (SWT) offer non-invasive treatments for chronic pain, musculoskeletal disorders, and sports injuries. AWT uses low-intensity sound waves to stimulate tissue repair, ideal for gentle pain reduction and function restoration. SWT employs higher-energy shockwaves to break up scar tissue and improve blood flow, enhancing recovery. Both therapies have minimal downtime; AWT incorporates stretching and strengthening exercises, while SWT focuses on improving range of motion post-treatments.
Acoustic Wave Therapy (AWT) and Shockwave Therapy are non-invasive treatments gaining traction in modern medicine. AWT uses low-intensity sound waves to stimulate tissue repair, while Shockwave Therapy employs higher-energy pulses for similar purposes. This article delves into the fundamental differences between these two therapies. We explore AWT’s gentle approach and its suitability for various conditions, contrasting it with Shockwave Therapy’s mechanism and specialized applications. By understanding their unique features, patients can make informed decisions about which therapy aligns best with their needs.
- Understanding Acoustic Wave Therapy: A Non-Invasive Approach
- Shockwave Therapy: Its Mechanism and Applications
- Key Differences: Unraveling the Distinctions Between the Two Therapies
Understanding Acoustic Wave Therapy: A Non-Invasive Approach
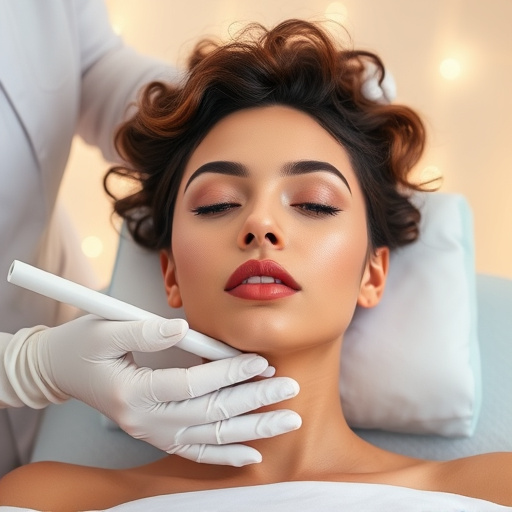
Acoustic Wave Therapy (AWT) represents a groundbreaking non-invasive approach to managing various health conditions, particularly focusing on chronic pain relief. Unlike many other therapies that involve incisions or injections, AWT leverages acoustic waves—high-intensity sound waves—to stimulate tissue repair and promote healing. This innovative technique has gained prominence in the medical field due to its ability to offer personalized treatment plans tailored to individual needs, making it a versatile solution for various ailments.
The beauty of AWT lies in its gentleness and safety. It doesn’t cause any pain or tissue damage, making it an attractive option for those seeking a non-invasive treatment with minimal side effects. By targeting specific areas, acoustic waves can effectively stimulate cellular activity, enhancing natural healing processes. This method has proven particularly effective in managing musculoskeletal disorders, sports injuries, and even certain skin conditions, ensuring patients receive the chronic pain relief they need without undergoing invasive procedures.
Shockwave Therapy: Its Mechanism and Applications
Shockwave Therapy, a non-invasive treatment approach, leverages high-energy acoustic waves to target tissues at the cellular level. This innovative therapy mechanism involves emitting focused sound waves that penetrate deep into the body, where they interact with cells and structures, stimulating healing responses. The energy from these shockwaves promotes angiogenesis—the growth of new blood vessels—and triggers the release of growth factors, essential chemicals that accelerate tissue repair and regeneration.
This therapy has found applications across various fields, including physical therapy, chiropractic care, and sports medicine. It is particularly effective for conditions such as tendon injuries, muscle strains, and chronic pain syndromes. By enhancing natural healing processes, shockwave therapy offers a safe and non-invasive alternative to surgical interventions, making it an attractive option for individuals seeking conservative treatment approaches.
Key Differences: Unraveling the Distinctions Between the Two Therapies
Acoustic Wave Therapy (AWT) and Shockwave Therapy (SWT) both offer non-invasive treatment options for various conditions, but they differ significantly in their mechanisms and applications. AWT utilizes low-intensity sound waves to stimulate tissue repair and promote healing, making it particularly effective for conditions like chronic back pain and sciatica relief without the side effects sometimes associated with drugs or surgery. In contrast, SWT employs higher-energy shockwaves to break up scar tissue and stimulate blood flow, which is more commonly used to treat musculoskeletal injuries and sports-related injuries, helping to accelerate the body’s natural healing process.
While both therapies are relatively non-invasive and have minimal downtime, AWT tends to focus on restoring function and reducing pain through gentle stimulation, whereas SWT aims to break down obstructions in the body, such as chronic scar tissue, to allow for better circulation and faster recovery. Therapeutic exercises may complement either therapy, but the specific approaches differ; AWT often incorporates tailored stretching and strengthening routines to support healing, while SWT may include specialized movements to improve range of motion after treatment sessions.
Acoustic Wave Therapy (AWT) and Shockwave Therapy (SWT) offer non-invasive treatment options with distinct mechanisms. AWT uses low-intensity sound waves to stimulate cellular repair, making it versatile for various conditions. SWT, on the other hand, employs high-energy shockwaves to promote healing by opening micro-channels in tissues. While both have shown effectiveness, AWT stands out for its gentle approach and broader applicability, whereas SWT is particularly suited for specific conditions like tendonitis and bone regeneration. Understanding these differences is crucial when selecting the most appropriate therapy for individual patient needs.